# Solution configuration
The solution, shown in the figure below, deploys a Rancher admin cluster and a number of supporting nodes external to the cluster, for load balancing and DHCP services. The solution also deploys a user cluster with optional CSI storage.
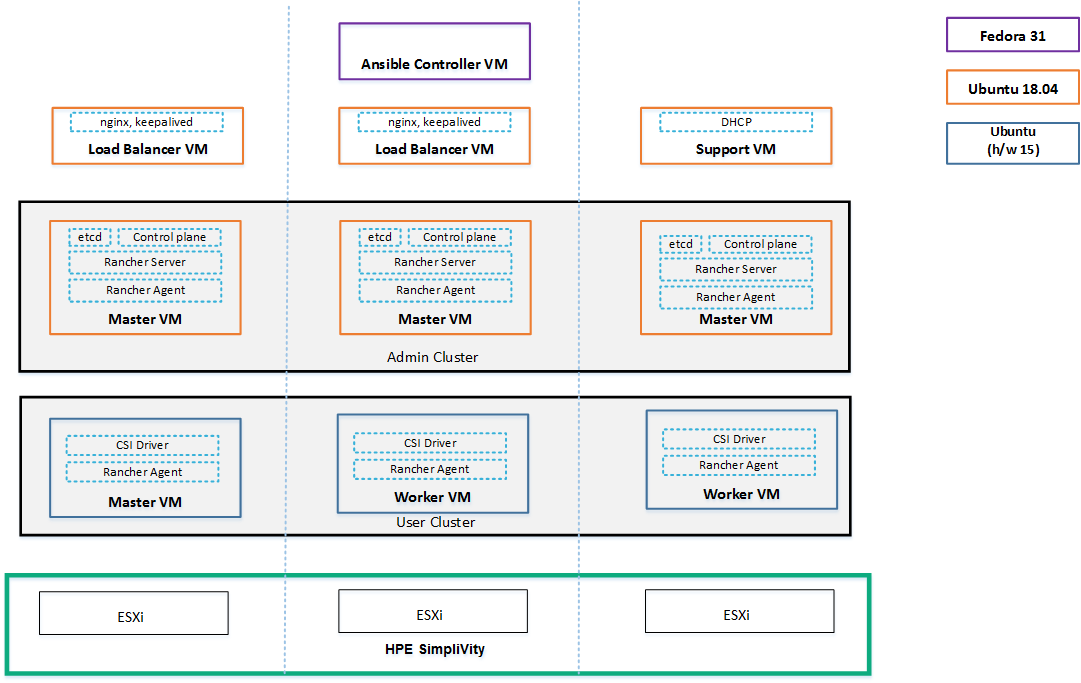
Figure. Rancher on HPE SimpliVity architecture
For Rancher v2.3.*, Rancher is installed on an RKE (Rancher Kubernetes Engine) Kubernetes cluster. RKE is a CNCF-certified Kubernetes distribution that runs entirely within Docker containers.
In a standard installation, Kubernetes is first installed on three nodes. Then Helm is used to install Rancher on top of the Kubernetes cluster. Helm uses Rancher’s Helm chart to install a replica of Rancher on each of the three nodes in the Kubernetes cluster. A load balancer is used to direct traffic to each replica of Rancher in the cluster, in order to increase Rancher’s availability.
The Rancher server data is stored on etcd. The etcd database component is a distributed key-value store used as Kubernetes storage for all cluster data, such as cluster coordination and state management. This etcd database also runs on all three nodes, and requires an odd number of nodes so that it can always elect a leader with a majority of the etcd cluster. If the etcd database cannot elect a leader, etcd can fail, requiring the cluster to be restored from backup.
A DNS record is required to map a URL to the load balancer. This will become the Rancher server URL, and downstream Kubernetes clusters will need to reach it.
RKE will need to connect to each node over SSH, and it will look for a private key in the default location of ~/.ssh/id_rsa.
