# Using Cloud Console to access your user clusters
This page explains how to log in to registered Kubernetes clusters from Google Cloud Console. The deployment playbooks register your clusters with Google Cloud, so you can log in to clusters from Cloud Console.
You can log in to registered clusters via Google Cloud Console using a bearer token. The easiest method is to create a Kubernetes service account in the cluster, and use its bearer token to log in.
# Utility script
A utility script create-user-gcp.sh is provided in the folder Anthos-on-SimpliVity/scripts/cluster-util to automate
the procedure to create a user in an Anthos user cluster and to assign view, node-reader
and cluster-admin (optional) roles:
./create-user-gcp.sh -h
This script is used to create a user in an Anthos user cluster and assign
view, node-reader and cluster-admin (Optional) roles
Syntax: create-user-gcp.sh [-n|a|h]
options:
-u Username to create in cluster. (Required)
-k Path to user cluster kubeconfig file. Will use env KUBECONFIG if set (Optional)
-A Set user as cluster admin. (Optional)
-h Print this Help.
Run this script on the admin workstation to create users and admins for the cluster determined by the kubeconfig.
# Manual procedure
The remainder of this page will walk through the equivalent manual steps required to create users.
# Connect to your admin workstation
ssh -i /root/anthos_secrets/vsphere_workstation ubuntu@10.15.155.200
# Configure KUBECONFIG
Configure kubectl to access the appropriate user cluster. For example:
export KUBECONFIG=~/kubeconfigs/gmcg-gke-usercluster-1-kubeconfig
# Create node-reader cluster role
Create a file called node-reader.yaml with the following content:
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: node-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
Create the new cluster role with the command:
kubectl apply -f node-reader.yaml
# Creating and authorizing a service account
Create a service account for each user logging in to the cluster. Using a bearer token is like using a password, so each user should have their own. Logging in with the service account's bearer token causes all operations to be executed as the KSA, restricted by the RBAC roles held by the service account.
Create the Kubernetes Service Account and ClusterRoleBinding resources to bind the view and node-reader Kubernetes RBAC ClusterRoles to the service account:
kubectl create serviceaccount test-user-sa
kubectl create clusterrolebinding test-user-sa-view --clusterrole view --serviceaccount default:test-user-sa
kubectl create clusterrolebinding test-user-sa-node-reader --clusterrole node-reader --serviceaccount default:test-user-sa
Determine the appropriate secret name:
kubectl get serviceaccount test-user-sa -o jsonpath='{$.secrets[0].name}'
test-user-sa-token-mnxjx
To acquire the bearer token for the service account, use the secret name in the following command:
kubectl get secret test-user-sa-token-mnxjx -o jsonpath='{$.data.token}' | base64 -d
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6Ik05ZWtZRTdhe ... hBDc6Q
Log in to the console at https://console.cloud.google.com/kubernetes/list:
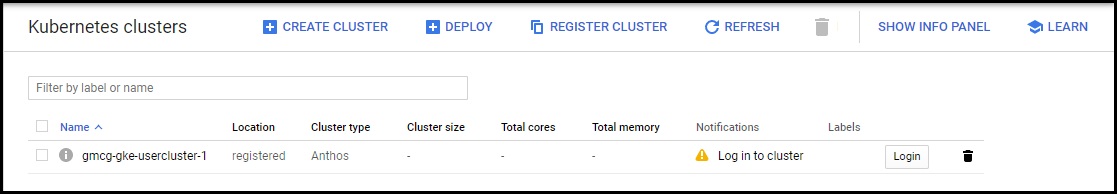
Figure. Cloud console - user cluster
Press the Login button and choose Token as the method you want to use for authentication to the cluster:
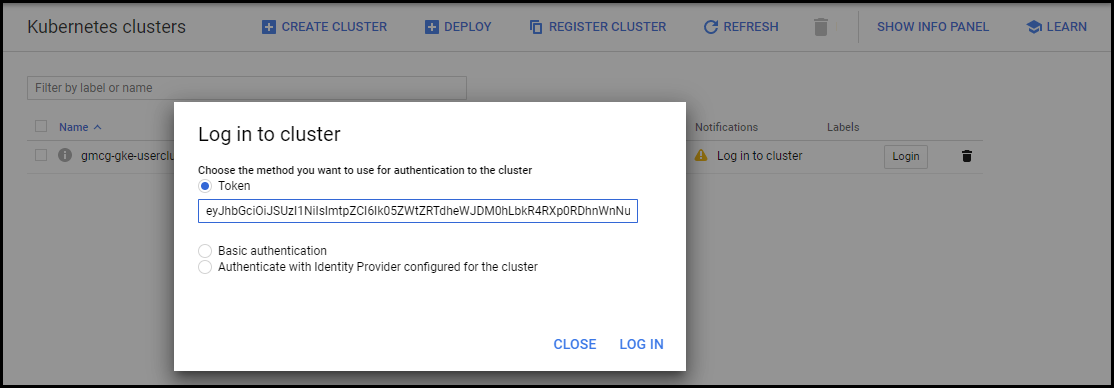
Figure. Cloud console - Login
Once you are authenticated, you can view the details for the on-prem user cluster:
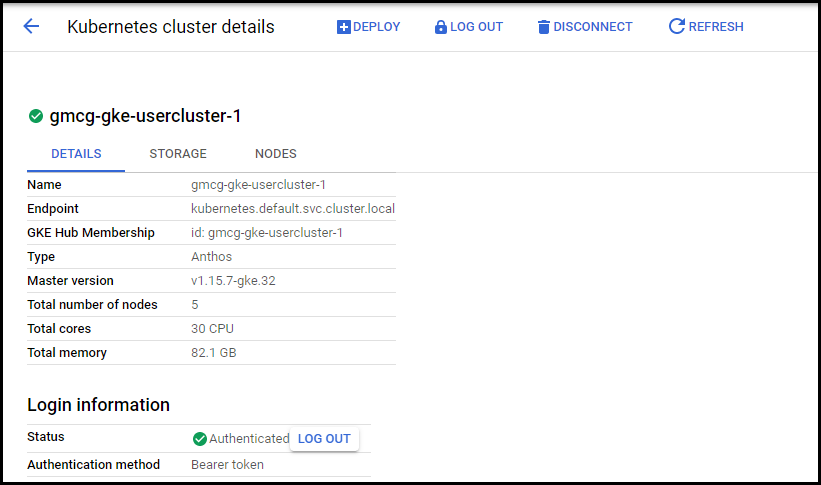
Figure. Cloud console - user cluster details
Click on the Nodes tab to see details of the individual nodes for the on-prem user cluster:
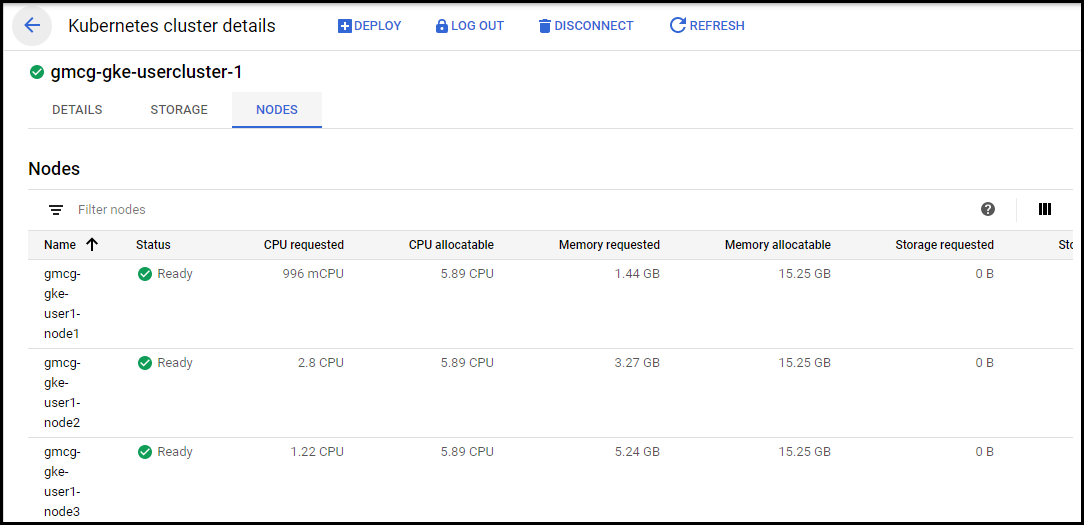
Figure. Cloud console - user cluster nodes
# Creating a cluster-admin role
The procedure is the same as above, except with the additional cluster-admin role:
kubectl create serviceaccount test-admin-sa
kubectl create clusterrolebinding test-admin-sa-view --clusterrole view --serviceaccount default:test-admin-sa
kubectl create clusterrolebinding test-admin-sa-node-reader --clusterrole node-reader --serviceaccount default:test-admin-sa
kubectl create clusterrolebinding test-admin-sa-admin --clusterrole cluster-admin --serviceaccount default:test-admin-sa
Determine the appropriate secret name:
kubectl get serviceaccount test-admin-sa -o jsonpath='{$.secrets[0].name}'
test-admin-sa-token-ndf5x
To acquire the bearer token for the service account, use the secret name in the following command:
kubectl get secret test-user-sa-token-ndf5x -o jsonpath='{$.data.token}' | base64 -d
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI...1kGgErzAVIjbM75CCOag
# Resources
# Google Cloud documentation
Logging in to a cluster from Cloud Console
https://cloud.google.com/anthos/multicluster-management/console/logging-in
