# Cluster ingress
This page describes the use of a number of methods used to enable access to cluster services including:
- ClusterIP
- Service endpoints
- NodePort
- Ingress
For information on LoadBalancer, see the section Deploying an application.
# Connect to your admin workstation
ssh -i /root/anthos_secrets/vsphere_workstation ubuntu@10.15.155.200
# Configure KUBECONFIG
Configure KUBECONFIG, using the appropriate user cluster name:
export KUBECONFIG=~/kubeconfigs/gmcg-gke-usercluster-1-kubeconfig
# Create deployment
Create a manifest file named hello-deployment.yaml with the following content:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
greeting: hello
replicas: 3
template:
metadata:
labels:
greeting: hello
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-world
image: "gcr.io/google-samples/hello-app:2.0"
env:
- name: "PORT"
value: "50000"
- name: hello-kubernetes
image: "gcr.io/google-samples/node-hello:1.0"
env:
- name: "PORT"
value: "8080"
The deployment specifies two continers in each pod. The first container hello-app responds with , while the second container node-hello responds with .
Create the deployment using the manifest:
kubectl apply -f hello-deployment.yaml
# Create a service
You can expose your deployment to clients outside your cluster using a Kubernetes service of type NodePort.
Create a manifest file named hello-service.yaml with the following content:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hello-service
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
greeting: hello
ports:
- name: world-port
protocol: TCP
port: 60000
targetPort: 50000
- name: kubernetes-port
protocol: TCP
port: 60001
targetPort: 8080
In the preceding example Deploying an application, the type of service was LoadBalancer and you
specified a loadBalancerIP.
In this instance, you create a service of type NodePort. This opens a specific port on all the nodes in the user
cluster, and any traffic that is sent to this port is forwarded to the service. While you can explicitly set a specific
port to open on the nodes, using the nodePort field, it is better to allow Kubernetes to assign a random port.
Create the service:
kubectl apply -f hello-service.yaml
# Service details
Display a summary of the service:
kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
hello-service NodePort 10.98.60.245 <none> 60000:31712/TCP,60001:30536/TCP 21s
For more details, use kubectl describe:
kubectl describe svc hello-service
Name: hello-service
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Service","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"hello-service","namespace":"default"},"spec":{"ports":[{"name":"w...
Selector: greeting=hello
Type: NodePort
IP: 10.98.60.245
Port: world-port 60000/TCP
TargetPort: 50000/TCP
NodePort: world-port 31712/TCP
Endpoints: 192.168.1.10:50000,192.168.3.20:50000,192.168.4.4:50000
Port: kubernetes-port 60001/TCP
TargetPort: 8080/TCP
NodePort: kubernetes-port 30536/TCP
Endpoints: 192.168.1.10:8080,192.168.3.20:8080,192.168.4.4:8080
Session Affinity: None
External Traffic Policy: Cluster
Events: <none>
# Using ClusterIP
Connect to one of your cluster nodes, as described in Using SSH to connect to cluster nodes:
ssh -i ~/.ssh/gmcg-gke-usercluster-1.key ubuntu@10.15.155.121
Access the hello-app container using the ClusterIP 10.98.60.245 and the port value 60000 set in the deployment manifest:
curl 10.98.60.245:60000
Hello, world!
Version: 2.0.0
Hostname: hello-deployment-79d7c89847-g7cpj
Access the second container, node-hello, again using the ClusterIP 10.98.60.245 but with port value 60001:
curl 10.98.60.245:60001
Hello Kubernetes!
# Using endpoints
There are three endpoints for accessing each container, since the deployment specified replicas: 3 for the number of
pods to create.
You can access the hello-app container using one of the three endpoints for the port named world-port:
kubectl describe svc hello-service
Name: hello-service
...
Port: world-port 60000/TCP
TargetPort: 50000/TCP
Port: world-port 60000/TCP
Endpoints: 192.168.1.10:50000,192.168.3.20:50000,192.168.4.4:50000
Connect to one of your cluster nodes using ssh, choose one of the endpoints using the targetPort of 50000 and use curl:
curl 192.168.1.10:50000
Hello, world!
Version: 2.0.0
Hostname: hello-deployment-79d7c89847-g7cpj
You can access the second container, node-hello using one of the three endpoints for the port named kubernetes-port:
kubectl describe svc hello-service
Name: hello-service
...
Port: kubernetes-port 60001/TCP
TargetPort: 8080/TCP
NodePort: kubernetes-port 30536/TCP
Endpoints: 192.168.1.10:8080,192.168.3.20:8080,192.168.4.4:8080
Connect to one of your cluster nodes using ssh, choose one of the endpoints using the targetPort of 8080 and use curl:
curl 192.168.1.10:8080
Hello Kubernetes!
# Alternative to using ssh for curl
Instead of using SSH to access the user cluster, you could deploy an image using kubectl on the admin workstation:
kubectl run curl --image=radial/busyboxplus:curl -i --tty
You can then test access to the containers using either the ClusterIP with the port or the endpoints with the targetPort, for example:
[ root@curl-6bf6db5c4f-qc7t4:/ ]$ curl 10.98.60.245:60000
Hello, world!
Version: 2.0.0
Hostname: hello-deployment-79d7c89847-m7lzr
# Using NodePort
A service of type NodePort opens a specific port on all the nodes in the user
cluster, and any traffic that is sent to this port is forwarded to the service.
Determine the addresses of the nodes in your user cluster, using the -o wide option:
kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
gmcg-gke-user1-node1 Ready <none> 7d18h v1.16.8-gke.6 10.15.155.121 10.15.155.121 Ubuntu 18.04.4 LTS 5.3.0-53-generic docker://19.3.2
gmcg-gke-user1-node2 Ready <none> 7d18h v1.16.8-gke.6 10.15.155.122 10.15.155.122 Ubuntu 18.04.4 LTS 5.3.0-53-generic docker://19.3.2
gmcg-gke-user1-node3 Ready <none> 7d18h v1.16.8-gke.6 10.15.155.123 10.15.155.123 Ubuntu 18.04.4 LTS 5.3.0-53-generic docker://19.3.2
gmcg-gke-user1-node4 Ready <none> 7d18h v1.16.8-gke.6 10.15.155.124 10.15.155.124 Ubuntu 18.04.4 LTS 5.3.0-53-generic docker://19.3.2
gmcg-gke-user1-node5 Ready <none> 2d21h v1.16.8-gke.6 10.15.155.125 10.15.155.125 Ubuntu 18.04.4 LTS 5.3.0-53-generic docker://19.3.2
Use the nodePort for the hello-world container with the IP address of a node in your user cluster:
curl 10.15.155.121:31712
Hello, world!
Version: 2.0.0
Hostname: hello-deployment-79d7c89847-g7cpj
Similarly, use the nodePort for the node-hello container with the IP address of a node in your user cluster:
curl 10.15.155.121:30536
Hello Kubernetes!
# Creating an Ingress
As part of creating your user cluster, you specified a virtual IP address (VIP) for ingress by providing a value for gke_cluster_config.cluster_ingress_vip for each cluster in your configuration file.
When a client sends a request to your user cluster ingress VIP, the request is routed to your F5 BIG-IP load balancer. The load balancer forwards the request to an ingress Service running in your user cluster. The ingress Service is configured to forward the request to different backends depending on the path in the request URL.
It is important to understand that there are two different Services related to the steps in this topic:
- Your Service named
hello-service. This is a Service that you created to expose the Pods of yourhello-deploymentDeployment. - The ingress Service that runs in the
gke-systemnamespace of your user cluster. This Service is part of your cluster infrastructure.
# Enabling Ingress
You must first enable Ingress on your Anthos GKE on-prem user cluster. For more information see the documentation at https://cloud.google.com/anthos/gke/docs/on-prem/how-to/enable-ingress.
For this example, you can create a file called ingress-gateway.yaml:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: istio-autogenerated-k8s-ingress
namespace: gke-system
spec:
selector:
istio: ingress-gke-system
servers:
- port:
number: 80
protocol: HTTP2
name: http
hosts:
- "*"
Create this Gateway:
kubectl apply -f ingress-gateway.yaml
You should now see in your F5 web console, that the virtual server for gke-system_istio-ingress-80-tcp is now enabled:
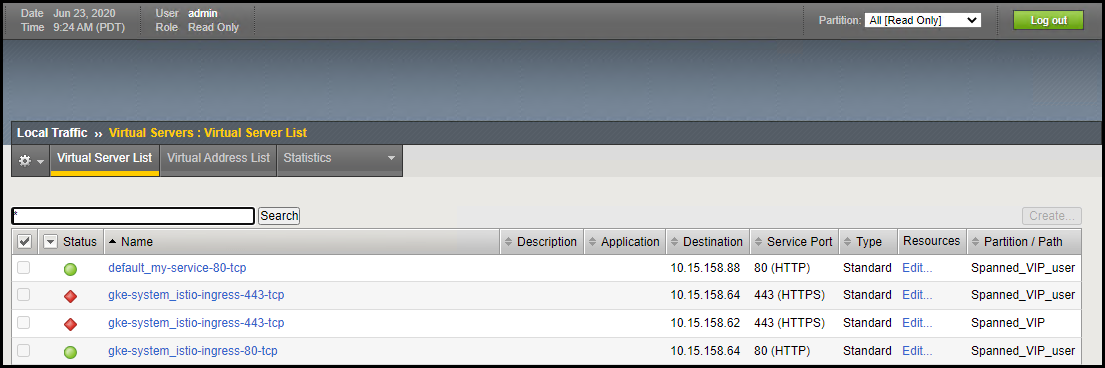
Figure. Ingress virtual service
# Using Ingress
Create a manifest named my-ingress.yaml with the content below:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: my-ingress
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /greet-the-world
backend:
serviceName: hello-service
servicePort: 60000
- path: /greet-kubernetes
backend:
serviceName: hello-service
servicePort: 60001
Deploy the Ingress service:
kubectl apply -f my-ingress.yaml
The Ingress resource maps the path /greet-the-world to port:60000 in the Service you created earlier. Using
the ingress VIP on the external network and the path /greet-the-world, you will access the hello-world container:
curl 10.15.158.64/greet-the-world
Hello, world!
Version: 2.0.0
Hostname: hello-deployment-79d7c89847-h6q4z
The Ingress resource maps the path /greet-kubernetes to port:60000 in the Service that you created earlier. Using
the ingress VIP on the external network and the path /greet-kubernetes, you will access the node-hello container:
curl 10.15.158.64/greet-kubernetes
Hello Kubernetes!
