Solution Components
Physical components
This section includes the hardware, software, and service components for the NGS-optimized solution for RHOCP.
Hardware
The following table includes the hardware requirements for this solution:
TABLE 2. Hardware components required for NGS-optimized solution for RHOCP
| Component | Qty | Description |
|---|---|---|
| HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen11 server | 3 | Provides capacity for head nodes with openshift master and bootstrap KVM vm’s,haproxy,dns,proxy |
| HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen11 server | 3 | Provide OpenShift worker nodes |
| HPE ProLiant DL380a Gen11 server | 3 | Provide OpenShift worker nodes for GPU based workloads |
| HPE Alletra MP | 1 | External iSCSI storage for Persistent Volumes |
| HPE Aruba 8325 switch | 2 | A network switch for datacenter network |
| HPE Aruba 6300M switch | 1 | A network switch for iLO Management network |
| HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen11 server | 3 | Red OpenShift Data Foundation nodes – Internal storage mode Red OpenShift Data Foundation nodes – External storage mode |
Software
NOTE
The installation user must ensure that they have downloaded or have access to these software components. Ensure that the appropriate subscriptions and licensing are in place to use within the planned time frame.
TABLE 3. Software requirements for NGS-optimized solution for RHOCP
| Component | Version |
|---|---|
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) | 4.16 |
| Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform (RHOCP) | 4.16 |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux | 9.4 |
| HPE Alletra 6k | 6.0.0.300-956221-opt |
| Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation | 4.16 |
TABLE 4. Switches for NGS-optimized solution for RHOCP
| Component | Version |
|---|---|
| Aruba 6300 | 10.10.1030 |
| Aruba 8325 | 10.10.1030 |
The following software must be available on the installer machine:
TABLE 5. Software requirements for the installer machine
| Component | Version |
|---|---|
| Ansible | 2.15.12 |
| Python | 3.9 |
| Java | 1.8 |
| Bind DNS | 9.11.36 |
| Squid Proxy | 4.16 |
| HAProxy | 1.8.27 |
| Chrony | 4.2 |
| Matchbox | 0.9 |
Services
This document is built with assumptions about services and network ports available within the implementation environment. This section discusses these assumptions.
The following table includes a list of services required for the NGS-optimized solution for RHOCP and provides a brief description of their function:
TABLE 6. Services used for the NGS-optimized solution for RHOCP
| Service | Description/Notes |
|---|---|
| BindDNS | Provides name resolution on management and data center networks. Domain Name Services must be in place for the management and data center networks. Ensure that both forward and reverse lookups are working for all hosts. |
| HAPROXY | HAProxy is a free, very fast and reliable reverse-proxy offering high availability, load balancing, and proxying for TCP and HTTP-based applications. |
| NTP | Ensures consistent time across the solution stack. A Network Time Protocol (NTP) server should be available for time synchronization to host within the solution environment. |
| DHCP | DHCP server provides IP addresses lease |
| iPXE | Enables booting of operating systems. Since all the nodes in this solution are booted using iPXE server, it is necessary to have a properly configured iPXE server. |
| KVM | Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) is an open-source virtualization technology. Specifically, KVM a hypervisor that allows a host machine to run multiple, virtual environments called guests or Virtual Machines (VMs). |
| Squid Proxy | Squid is a web proxy server application that gives organizations proxy and cache services for the Web supporting HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and more. |
| Keepalived | Keepalived is used for IP failover between two servers. Its facilities for load balancing and high-availability to Linux-based infrastructures. It worked on Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) protocol. |
DHCP
DHCP should be present on RHEL8 Installer VM and able to provide IP address leases for iPXE deployment of RHCOS on worker nodes.
Network port
The port information listed in Table 7 allows cluster components to communicate with each other.
To retrieve this information from bootstrap, master, and worker nodes, run the following command:
> netstat –tupln
The following table shows a list of network ports used by the services under RHOCP 4.16.
TABLE 7. Network ports used by RHOCP 4.16 services
| Protocol | Port Number/Range | Service Type | Other details |
|---|---|---|---|
| TCP | 80 | HTTP Traffic | |
| 443 | HTTPS traffic | ||
| 2379-2380 | etcd server, peer and metrics ports | ||
| 6443 | Kubernetes API | The Bootstrap machine and masters. | |
| 9000-9999 | Host level services, including the node exporter on ports 9100-9101 and the Cluster Version Operator on port 9099. | ||
| 10249-10259 | The default ports that Kubernetes reserves. | ||
| 10256 | openshift-sdn | ||
| 22623 | Machine Config Server | The Bootstrap machine and masters. | |
| UDP | 4789 | VXLAN and GENEVE | |
| 6081 | VXLAN and GENEVE | ||
| 9000-9999 | Host level services, including the node exporter on ports 9100-9101 | ||
| 30000-32767 | Kubernetes NodePort | ||
| TCP | 3128 | Squid Proxy | Squid is a caching and forwarding web proxy |
| TCP/UDP | 53 | Bind DNS | BIND can be used to run a caching DNS server or an authoritative name server, and provides features like load balancing, notify, dynamic update, split DNS, DNSSEC, IPv6, and more. |
For more information on the network port requirements for RHOCP 4.16, see the Networking requirements for user-provisioned infrastructure section in the OpenShift Container Platform 4.16 documentation.
Networking components
The following figure illustrates the cabling configuration of the three HPE ProLiant AMD and Intel servers, Aruba 8360 and Aruba 6300 switches, and Intelligent Resilient Fabric (IRF) for the NGS-optimized solution for RHOCP. These cables carry frame management, inter-frame, and interconnect traffic between frames.
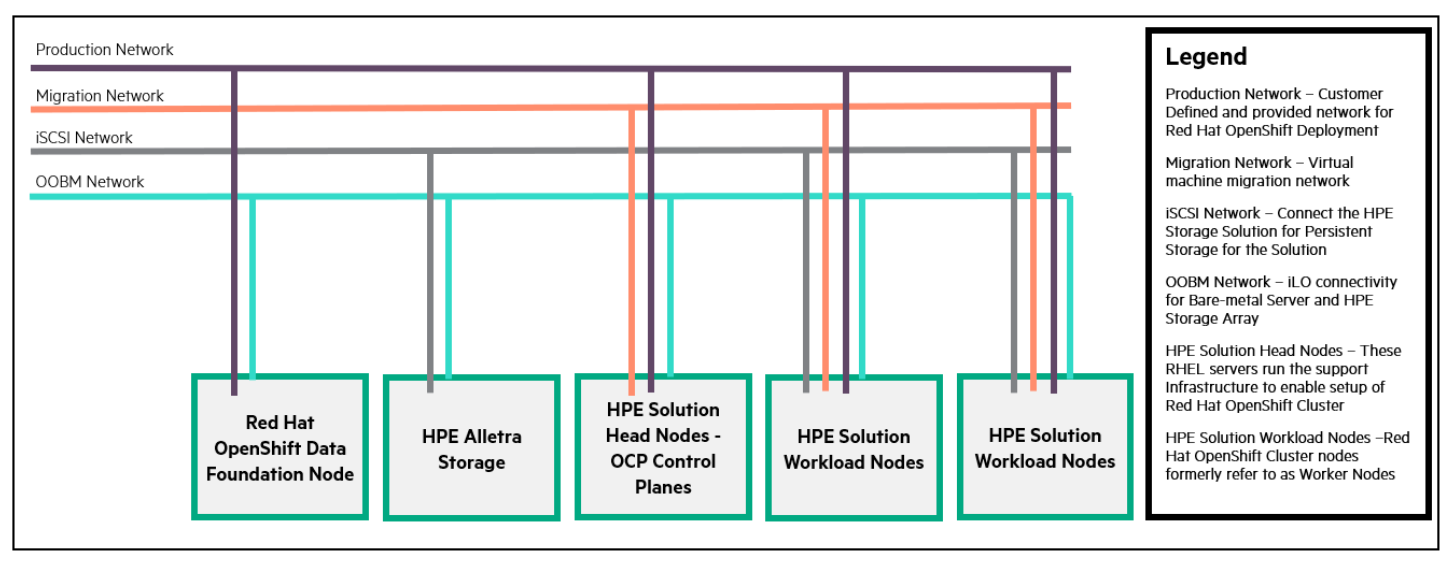
FIGURE 4. NGS-optimized solution for RHOCP 4.16 – Network configuration
The NGS-optimized solution for RHOCP network configuration includes the following components:
- Production Network: It is customer defined and provides networks for RHOCP deployment.
- Migration Network: A network provisioned for migration of virtual machines.
- ISCSI Network: It includes dedicated networks optimized for lossless compute to storage communication.
- OOBM Network: It provides iLO for servers and Block Storage Management and connects to the OOBM management switch.
Storage components
This section includes storage components that are required for the NGS-optimized solution for RHOCP.
HPE CSI Driver for HPE Alletra Storage
The HPE Container Storage Interface (CSI) Driver for Kubernetes is a multi-vendor and multi-platform driver that adds and configures platforms using a component, known as the Container Storage Provider (CSP). THPE Alletra Storage MP hardware and managed via the HPE GreenLake cloud platform.
HPE CSI was developed as a standard for exposing block and file storage systems to containerized workloads on Container Orchestrator Systems (COS) like Kubernetes. This standard is an initiative to unify the COS storage interface with the storage vendors. For example, a single HPE CSI implemented for a storage vendor is guaranteed to work with all COS.
HPE CSI Driver architecture
Figure 5 is a diagrammatic representation of the HPE CSI Driver architecture:

FIGURE 5. HPE CSI Driver architecture
CSI Deployment Workflow
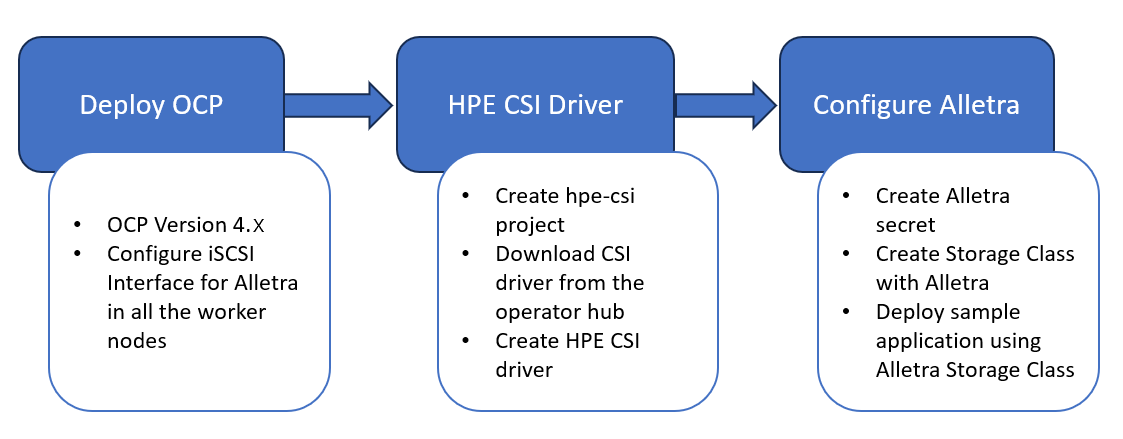
FIGURE 6. High-level flow diagram for HPE CSI Driver deployment on RHOCP 4.16
The Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform (RHOCP) 4.16 cluster includes physical master and worker nodes running RHEL 9.4 as the operating system. The iSCSI interface configured on the host nodes establishes the connection with the HPE Alletra array to the cluster. After the successful deployment of HPE CSI Driver, CSI controller, 3PAR CSP, and Nimble CSP are deployed to communicate with the HPE Alletra arrays via REST APIs. The associated features on Storage Class such as CSI provisioner, CSI attacher, and so on are configured on the Storage Class.