# Rancher user cluster configuration
Once the admin cluster has been deployed and Rancher server has been installed, the playbooks deploy a user cluster based on the following configuration.
# General config for user cluster
| Variable | File | Description |
|---|---|---|
user_folder | group_vars/all/vars.yml | Folder and pool name for the user cluster VMs |
user_cluster.name | group_vars/all/vars.yml | The name of the user cluster |
user_cluster.vcenter_credsname | group_vars/all/vars.yml | The name given to the generated Cloud Credentials |
user_cluster.csi | group_vars/all/vars.yml | Boolean. Set to true to configure the CSI driver on the user cluster |
user_cluster.vm_template | group_vars/all/vars.yml | The VM template to use when creating the nodes in the user cluster. Defaults to the admin template if none specified. |
If you want to use a different template for the user cluster and want to enable CSI support, be sure to set the
user_cluster.vm_template variable to an appropriate VM template that is available in the vSphere instance and is using
hardware compatibility version 15.
For more information on configuring the CSI driver for a user cluster, see the section Container Storage Interface (CSI) configuration.
The following figure shows the generated cloud credentials in the UI, accessed via your profile:
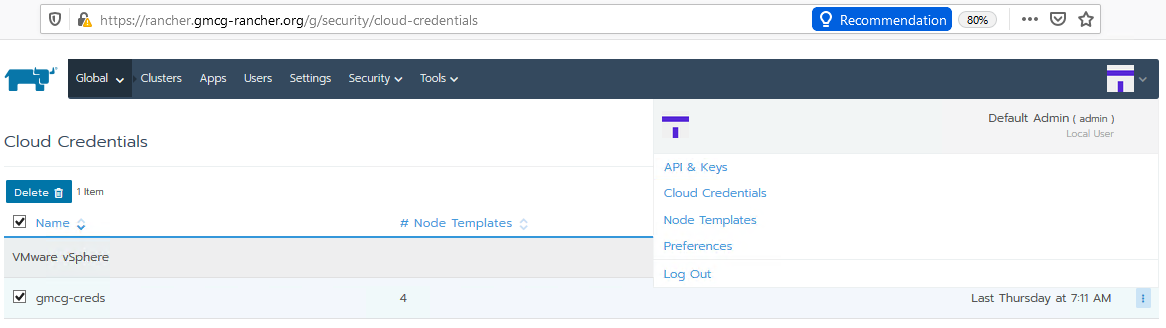
Figure. Cloud credentials
# Configuration of pools
user_cluster.pools is an array of pool configurations, with typically one pool specified for master nodes,
and one pool for worker nodes. Note that the cluster must have at least one master node, one etcd node and one worker node.
The configuration variables used within each pool definition are detailed below.
| Variable | File | Description |
|---|---|---|
name | group_vars/all/vars.yml | The name of the pool, for example master-pool or worker-pool |
etcd | group_vars/all/vars.yml | Boolean.true if you want etcd to run on nodes in this pool |
master | group_vars/all/vars.yml | Boolean.true if you want the nodes in this pool to be master nodes |
worker | group_vars/all/vars.yml | Boolean.true if you want the nodes in this pool to be worker nodesNote that a node can act as both a master and a worker node |
count | group_vars/all/vars.yml | Number of nodes of this type to create. |
hostPrefix | group_vars/all/vars.yml | The prefix used to identify these nodes as belonging to this pool Typically, you will specify a different prefix for master and worker nodes |
# Node templates
For each pool, a node template can be specified with resource configuration appropriate to the node type of the pool.
| Variable | File | Description |
|---|---|---|
node_template.name | group_vars/all/vars.yml | The name of the generated node template |
node_template.cpu_count | group_vars/all/vars.yml | The number of virtual CPUs for the node |
node_template.disk_size | group_vars/all/vars.yml | The size of disk in MB to create for the node |
node_template.memory_size | group_vars/all/vars.yml | The size of RAM in MB |
The following figure shows the generated node templates in the UI, accessed via your profile:
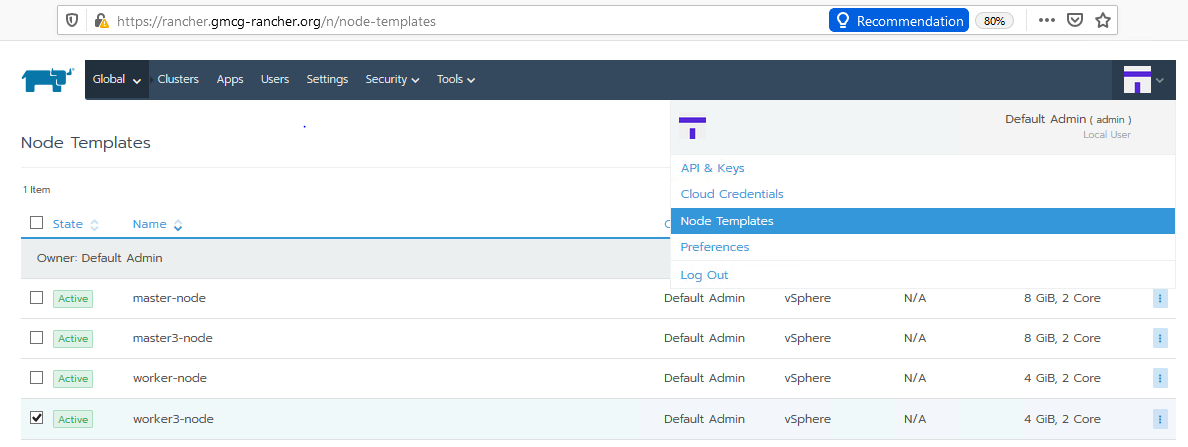
Figure. Node templates
# Sample user cluster definition
The sample definition has one master pool, with a single node containing the master and etcd components. There is also a single worker pool, with 2 nodes that only run worker components. In this example, the VM template is commented out, so the default is to use the same template as that used for the Rancher admin cluster.
user_cluster:
# vm_template: hpe-ubuntu-tpl
name: api
csi: false
vcenter_credsname: gmcg-creds
pools:
- name: master-pool
etcd: true
master: true
worker: false
count: 1
hostPrefix: hpe-mas
node_template:
name: master-node
cpu_count: 2
disk_size: 20000
memory_size: 8192
- name: worker-pool
etcd: false
master: false
worker: true
count: 2
hostPrefix: hpe-wrk
node_template:
name: worker-node
cpu_count: 2
disk_size: 40000
memory_size: 4096
